Home About Courses Admission Tutorials Contact
Programming Language:
1. What is Java programming language?
Java is a general-purpose computer programming language that is concurrent, class-based, object-oriented, and specifically designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is intended to let application developers “write once, run anywhere” (WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need for recompilation.
For example, you can write and compile a Java program on UNIX and run it on Microsoft Windows, Macintosh, or UNIX machine without any modifications to the source code.
WORA is achieved by compiling a Java program into an intermediate language called bytecode. The format of bytecode is platform-independent. A virtual machine, called the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), is used to run the bytecode on each platform.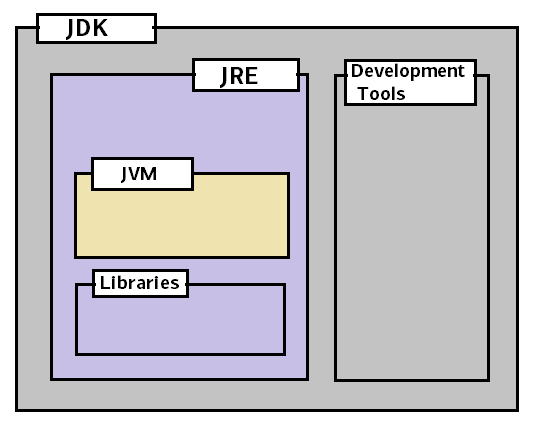
History of Java
Java was originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems (which has since been acquired by Oracle Corporation) and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems’ Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++, but it has fewer low-level facilities than either of them.
Oracle Corporation is the current owner of the official implementation of the Java SE platform, following their acquisition of Sun Microsystems on January 27, 2010. This implementation is based on the original implementation of Java by Sun. The Oracle implementation is available for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, Linux and Solaris.
The Oracle implementation is packaged into two different distributions:
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE) which contains the parts of the Java SE platform required to run Java programs and is intended for end users.
- Java Development Kit (JDK) which is intended for software developers and includes development tools such as the Java compiler, Javadoc, Jar, and a debugger.
Click here to learn JAVA Tutorials.
2. What is Python? Executive Summary
Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language with dynamic semantics. Its high-level built in data structures, combined with dynamic typing and dynamic binding, make it very attractive for Rapid Application Development, as well as for use as a scripting or glue language to connect existing components together. Python's simple, easy to learn syntax emphasizes readability and therefore reduces the cost of program maintenance. Python supports modules and packages, which encourages program modularity and code reuse. The Python interpreter and the extensive standard library are available in source or binary form without charge for all major platforms, and can be freely distributed.
Often, programmers fall in love with Python because of the increased productivity it provides. Since there is no compilation step, the edit-test-debug cycle is incredibly fast. Debugging Python programs is easy: a bug or bad input will never cause a segmentation fault. Instead, when the interpreter discovers an error, it raises an exception. When the program doesn't catch the exception, the interpreter prints a stack trace. A source level debugger allows inspection of local and global variables, evaluation of arbitrary expressions, setting breakpoints, stepping through the code a line at a time, and so on. The debugger is written in Python itself, testifying to Python's introspective power. On the other hand, often the quickest way to debug a program is to add a few print statements to the source: the fast edit-test-debug cycle makes this simple approach very effective.
Click here to learn Python Tutorials.
3. What is C++?
C++ is a general-purpose programming language. It was created by Bjarne Stroustrup at Bell Labs circa 1980. C++ is very similar to C (invented by Dennis Ritchie in the early 1970s). C++ is so much compatible with C that it will probably compile over 99% of C programs without changing a line of source code. Though, C++ is a lot well-structured and safer language than C as it OOPs based.
Some computer languages are written for a specific purpose. Like, Java was initially devised to control toasters and some other electronics. C was developed for programming OS. Pascal was conceptualized to teach proper programming techniques. But C++ is a general-purpose language. It well deserves the widely acknowledged nickname "Swiss Pocket Knife of Languages."
Click here to learn C++ tutorials.
Click here to learn C++ tutorials.
4. What is VBA?
VBA stands for Visual Basic for Applications. It is a combination of the Microsoft's event-driven programming language Visual Basic with Microsoft Office Applications such as Microsoft Excel.
VBA enables you to automate various activities in Excel like generating reports, preparing charts & graphs, doing calculations, etc. This automation activity is also often referred as Macro. This way it helps users to save their time spent behind running the repetitive steps.
Here is what we cover in the Course
| Tutorial | Introduction to Macros in Excel |
| Tutorial | Creating your First Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) in Excel |
| Tutorial | VBA Data Types, Variables & Constant |
| Tutorial | VBA Arrays |
| Tutorial | VBA Excel Form Control & Activex Control |
| Tutorial | VBA Arithmetic Operators |
| Tutorial | VBA String Operators |
| Tutorial | VBA Comparison Operators |
| Tutorial | VBA Logical Operators |
| Tutorial | Excel VBA Call a Subroutine |
| Tutorial | Excel VBA Function Tutorial: Return, Call, Examples |
| Tutorial | VBA Range Objects |
| Tutorial | Excel VBA Tutorial PDF Click here to learn VBA tutorials. |
5. What is MySQL?
MySQL, the most popular Open Source SQL database management system, is developed, distributed, and supported by Oracle Corporation.
The MySQL website (http://www.mysql.com/) provides the latest information about MySQL software.
MySQL is a database management system.
A database is a structured collection of data. It may be anything from a simple shopping list to a picture gallery or the vast amounts of information in a corporate network. To add, access, and process data stored in a computer database, you need a database management system such as MySQL Server. Since computers are very good at handling large amounts of data, database management systems play a central role in computing, as standalone utilities, or as parts of other applications.
MySQL databases are relational.
A relational database stores data in separate tables rather than putting all the data in one big storeroom. The database structures are organized into physical files optimized for speed. The logical model, with objects such as databases, tables, views, rows, and columns, offers a flexible programming environment. You set up rules governing the relationships between different data fields, such as one-to-one, one-to-many, unique, required or optional, and “pointers” between different tables. The database enforces these rules, so that with a well-designed database, your application never sees inconsistent, duplicate, orphan, out-of-date, or missing data.
The SQL part of “MySQL” stands for “Structured Query Language”. SQL is the most common standardized language used to access databases. Depending on your programming environment, you might enter SQL directly (for example, to generate reports), embed SQL statements into code written in another language, or use a language-specific API that hides the SQL syntax.
SQL is defined by the ANSI/ISO SQL Standard. The SQL standard has been evolving since 1986 and several versions exist. In this manual, “SQL-92” refers to the standard released in 1992, “SQL:1999” refers to the standard released in 1999, and “SQL:2003” refers to the current version of the standard. We use the phrase “the SQL standard” to mean the current version of the SQL Standard at any time.
MySQL software is Open Source.
Open Source means that it is possible for anyone to use and modify the software. Anybody can download the MySQL software from the Internet and use it without paying anything. If you wish, you may study the source code and change it to suit your needs. The MySQL software uses the GPL (GNU General Public License), http://www.fsf.org/licenses/, to define what you may and may not do with the software in different situations. If you feel uncomfortable with the GPL or need to embed MySQL code into a commercial application, you can buy a commercially licensed version from us. See the MySQL Licensing Overview for more information (http://www.mysql.com/company/legal/licensing/).
The MySQL Database Server is very fast, reliable, scalable, and easy to use.
If that is what you are looking for, you should give it a try. MySQL Server can run comfortably on a desktop or laptop, alongside your other applications, web servers, and so on, requiring little or no attention. If you dedicate an entire machine to MySQL, you can adjust the settings to take advantage of all the memory, CPU power, and I/O capacity available. MySQL can also scale up to clusters of machines, networked together.
MySQL Server was originally developed to handle large databases much faster than existing solutions and has been successfully used in highly demanding production environments for several years. Although under constant development, MySQL Server today offers a rich and useful set of functions. Its connectivity, speed, and security make MySQL Server highly suited for accessing databases on the Internet.
Click here to learn MySQL tutorials.
6. Golang Programming Language
Go is an open source programming language that makes it easy to build simple, reliable, and efficient software.
Announcing the 2019 Go Developer Survey
Since 2016, thousands of Gophers around the world have helped the Go project by sharing your thoughts via our annual Go Developer Survey. Your feedback has played an enormous role in driving changes to our language, ecosystem, and community, including the gopls language server, new error-handling mechanics, the module mirror, and so much more from the latest Go 1.13 release. And of course, we publicly share each year's results, so we can all benefit from the community's insights.
Published 20 November 2019
Go.dev: a new hub for Go developers
Over the last two years, as we’ve spoken with users at companies of all sizes, we’ve heard three questions repeatedly: who else is using Go, what do they use it for, and how can I find useful Go packages?
Published 13 November 2019
Announcing the 2019 Go Developer Survey
Todd Kulesza
20 November 2019
Help shape the future of Go
Since 2016, thousands of Gophers around the world have helped the Go project by sharing your thoughts via our annual Go Developer Survey. Your feedback has played an enormous role in driving changes to our language, ecosystem, and community, including the gopls language server, new error-handling mechanics, the module mirror, and so much more from the latest Go 1.13 release. And of course, we publicly share each year's results, so we can all benefit from the community's insights.
Today we are launching the 2019 Go Developer Survey. We'd love to hear from everyone who uses Go, used to use Go, or is interested in using Go, to help ensure the language, community, and ecosystem fit the needs of the people closest to it. Please help us shape Go's future by participating in this 15-minute survey by December 15th: Take the 2019 Go Developer Survey.
Spread the word!
We need as many Gophers as possible to participate in this survey to help us better understand our global user base. We'd be grateful if you would spread the word by sharing this post on your social network feeds, around the office, at meet-ups, and in other communities. Thank you!
Go.dev: a new hub for Go developers
Steve Francia and Julie Qiu
13 November 2019
Over the last two years, as we’ve spoken with users at companies of all sizes, we’ve heard three questions repeatedly: who else is using Go, what do they use it for, and how can I find useful Go packages?
Today we are launching go.dev, a new hub for Go developers, to help answer those questions. There you will find a wealth of learning resources to get started with the language, featured use cases, and case studies of companies using Go.
Click here to learn Golang tutorials.
7. Programming and Uses Of Ruby
Ruby is mainly designed or follow the principle of least astonishment (POLA). Its main idea is to reduce the complexity of use for users. While developing programmers can enjoy the programming in Ruby. Ruby has come up with great features like support to an object-oriented language, inheritance, garbage collection, dynamic and duck typing, overloading, exception handling, built-in support, support to all major platforms, compatible with other languages, and scope of variables, etc.
Ruby
Ruby is an open-source programming language. It is also referred to as scripting language that is dynamic, interpreted and object-oriented as well. It was created and developed by Yukihiro Matsumoto in the year 1993. It was first released or appeared in 1995. It supports cross-platform operating systems. It was written in C language. Ruby has a syntax that is mainly similar to Perl and Python. It is scalable and projects with large code are easily maintainable.
Top 10 Uses Of Ruby
There are many advantages to using Ruby. Below is the list of the top 10 Uses of Ruby.
1. Object
In Ruby, everything is an object. It means that every object in Ruby can be unique and having its own methods and properties as when the object of the class has been created, it can get its own class referred as a singleton. Ruby is simply executing the code with ‘self’ pointing at the class. It helps in evaluating the code in the class context from any location.
2. Modules
Uses of Ruby has different and awesome modules, which allow dynamic addition of new elements of the class hierarchy at runtime. The modules that are added can be evaluated dynamically at runtime and making much easier to extend the required functionality. Ruby also provides the lifecycle hooks, which allows using the modules effectively or robustly to isolate the extensions from one another.
3. Code development
In Ruby, it has been seen that the development code is much faster than other programming languages. In stats, ruby is not the fastest language for running and processing requests but developing the software products in ruby is way faster than other languages.
4. Dynamic Typing
Uses of Ruby has one of the great features that is dynamic typing, which means the type of variable can be changed and can be resolved on a fly at the time when parsed by an interpreter. Dynamic typing really helps the project while doing changes in further stages of development. Whereas in static typing, type of variable is defined and resolved by interpreter initially, which does not allow us to change the type further. So, dynamic typing plays a crucial role in different stages for the development of projects.
5. Duck Typing
In Ruby, Duck typing refers to be less concerned about the object of the class but mainly concerned with methods that can be called on and the operations that are going to perform on that methods. In ruby, we don’t declare the types of methods, everything is based on the object only and these ruby objects can be modified individually. We are mainly relying on the object capabilities, which helps in defining the type object.
6. Code Quality
Ruby code is intuitive, which provides the good quality code to the application and it is easier to read and write as well. The quality of code mainly depends on best practices followed and compliance with common standards. Ruby is perfectly tooled for testing an integral part of producing clean code. Ruby has a standard library that provides the complete suite of testing tools.
7. Maintainability
Ruby is intuitive, it makes easy for the developers to maintain and understand. It makes the code to run faster and quicker. It takes less effort of the programmers or developers to maintain the large piece of code and already written code can be used again means same code need not be writing every time. As the ruby code is easy to understand, it is very easy to track down the bugs and fix them quickly.
8. Performance and Security
Ruby has clean code while developing the application which makes its smooth and great performance without throwing any issues. The application runs faster because of this and it also provides or ensures the security of the application. Uses of Ruby ensures the high performance and secured deliverable of application for pleasant customer experience which makes it the first choice of developers to develop the application in Ruby.
9. Other features
It supports free format means writing of program can be started from any line and column. It is also case-sensitive means lowercase and uppercase letters are completely different. In ruby, # is being used if we want to comment anything means interpreter won’t take into consideration. In ruby, keywords are mainly referred to as reserve keywords. Multiple statements on one line must be separated with help of semicolon but it’s not required at the end of the line.
10. Community
Ruby has a great community which is very active, optimist and large. The community helps in every way out to help out the developers. It supports the new developers to learn with help of providing the material, books, courses, and other discussion platforms. It also maintains the applications of ruby and provides the latest information regarding the latest frameworks, libraries, and tools which are getting developed to make ruby better and because of which we can use ruby and develop the new applications for user or customer. Ruby has given the popular framework Ruby on Rails which is widely used among the developers for the development of applications.
Conclusion – Uses Of Ruby
Ruby was mainly designed as a general-purpose scripting language, which provides the wide support for the different applications of ruby. It is mainly getting used for a web application, standard libraries, servers, and other system utilities. Ruby has one of the great strength is metaprogramming. Ruby is getting popular now these days among the developers because of providing new frameworks for developing the application. It really helps in maintaining the code as well.
Ruby has more learning curve but it is easier to write and understand. So, the beginners or the students can learn it easily and quickly. Uses of Ruby is open source and easily available, which helps to use this language easily. The online community support and forums are also making the things simpler.
Click here to learn Ruby Tutorials.
8. PHP Programming and Uses:
Introduction to PHP Data Types
PHP (an acronym for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor) is an open-source scripting language used for web development and they contain HTML code embedded in them. This client-side scripting is different from others as the code is first executed on the server which generates the HTML then used by the client. It is hence used to develop Static and Dynamic Web applications. A PHP file has its extension as “.php”. Let us learn more about the data types used in PHP.
Top 3 PHP Data Types
PHP variables used to store values may be associated with all kinds of data types ranging from the simplest int to more complicated data types such as arrays. PHP is called a loosely typed Programming language, which means the variable data types are decided based on its attributes during run-time and is not explicitly defined. It analyses the attributes of the value given and then determines the data type to be assigned to it. There are 8 primitive data types which PHP supports and which can be further classified to 3 types as below:
Let us go through each one of them in detail with an example each.
1. Scalar Types
They can be further divided into primitive types as below:
a. Boolean
These types have their possible output in the form of either 0 or 1 i.e. true or false. They are used for conditional testing cases where the event returns true when the condition is satisfied and false when it does not satisfy. It also considers NULL and empty string as false.
Code:
<?php// TRUE is assigned to a variable value$variable_value = true;var_dump($variable_value);?>
Output:
b. Integer
An integer data type holds non-decimal whole number values between -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647. This maximum and minimum value depends on the system whether it is 32-bit or 64-bit. By using the constant PHP_INT_MAX we can find out the max value. Also holds base 10, base 8 and base 6 values.
Popular Course in this category

Related Courses
Code:
<?php// example for decimal (base 10)$dec1 = 100;$dec2 = 200;// example for decimal (base 8)$oct1 = 10;// example for decimal (base 6)$hex1 = 0x15;$addn = $dec1 + $dec2;echo $addn;?>
Output:
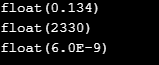
c. Float/ Double
A number having decimal point or an exponent is called a floating-point number/ real number. It can have both positive and negative numbers. There shall be a pre-defined number of decimal places displayed for the number.
Code:
<?php$dec1 = 0.134;var_dump($dec1);$exp1 = 23.3e2;var_dump($exp1);$exp2 = 6E-9;var_dump($exp2);?>
Output:
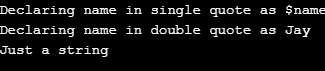
d. String
A string data type is basically a collection of characters including numbers, alphabets, and letters. They can hold values up to 2GB. They are to be declared using double quotes if a variable has to be displayed amongst the string. Else, a single quote also works.
Code:
<?php$name = "Jay";$str1 = 'Declaring name in single quote as $name';echo $str1;echo "\n";$str2 = "Declaring name in double quote as $name";echo $str2;echo "\n";$str3 = 'Just a string';echo $str3;?>
Output:
2. Compound Types
These are the ones for which new values cannot be assigned. Arrays and objects fall under this category.
a. Arrays
It is a data structure having a collection of fixed size of elements with similar data types. It is also used to store the known amount of key-value pairs in the form of an ordered map in it. It can be used for various purposes like a list, hash table (map implementation), collection, stack, dictionary, queue, etc, Multi-dimensional arrays are also possible.
A simple example of an array is as follows:
Code:
<?php$animals = array("Dog", "Cat", "Cow");var_dump($animals);$animal_babies = array("Dog" => "Puppy","Cat" => "Kitten","Cow" => "Calf");var_dump($animal_babies);?>
Output:
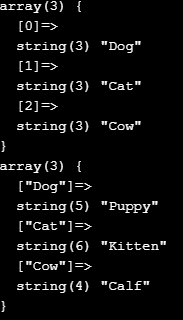
b. Objects
It allows to store data (called its properties) and also gives information on how to process (called the methods of the object) the same. An object serves as an instance of a class which is used as templates for other objects. The keyword “new” is used for the creation of an object.
Each object inherits the properties and methods from that of the parent class. It requires an explicit declaration and a “class” in each object.
Code:
<?php// Declaring a classclass statement{// propertiespublic $stmt = "Insert any string here";// Declaring a methodfunction show_statement(){return $this->stmt;}
}
// Creation of new object
$msg = new statement;
var_dump($msg);
?>
Output:
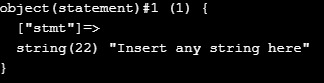
3. Special Types
There are 2 special data types in PHP which fall under this category since they are unique. They are:
a. NULL
In PHP, this special NULL is used for representing empty variables i.e. the variable has no data in it and NULL is the only possible value to it. A variable assigned to the constant NULL, if it has been set to unset() or if no value has been set to it becomes a NULL data type.
Here we are setting NULL directly to val1. Whereas, for the val2 variable, we are assigning a string value first and then set it as NULL. In both cases the final value of variables is NULL.
Code:
<?php$val1 = NULL;var_dump($val1);echo "<br>";$val2 = "Any string";$val2 = NULL;var_dump($val2);?>
Output:
b. Resources
Resource is not an actual data type whereas it is a special variable that keeps a reference to a resource external to PHP. They hold special handlers for files and database connections that are open. Special functions usually create and use these resources.
To run this code, we must have the file.txt created in the system with read permission given to it. It throws an error in case “handle” is not a resource. Also, make sure to connect to any existing database in your system.
Code:
<?php// Open an existing file to read$handle = fopen("file.txt", "r");var_dump($handle);echo "<br>";// Connecting to MySQL database server with settings set to default$db = mysql_connect("localhost", "root", "");var_dump($db);?>
Apart from the above data types, we also have something called pseudo-types which are the keywords in PHP document used to indicate the types or values which an argument can have. Some of them are:
- mixed: They allow a parameter to accept more than one type. Ex: gettype()
- number: With number, a parameter can be afloat or an integer.
- void, callback, array|object are some of the other pseudo-types
Conclusion
Here we have covered almost all of the data types which are available in PHP. All of the above 8 primitive types are implicitly supported by PHP and there is no need for the user to specify them manually. Arrays and objects can hold multiple values whereas for rest all can hold only a single value (except NULL which holds no value).
Click here to learn PHP Data Programming.








No comments:
Post a Comment